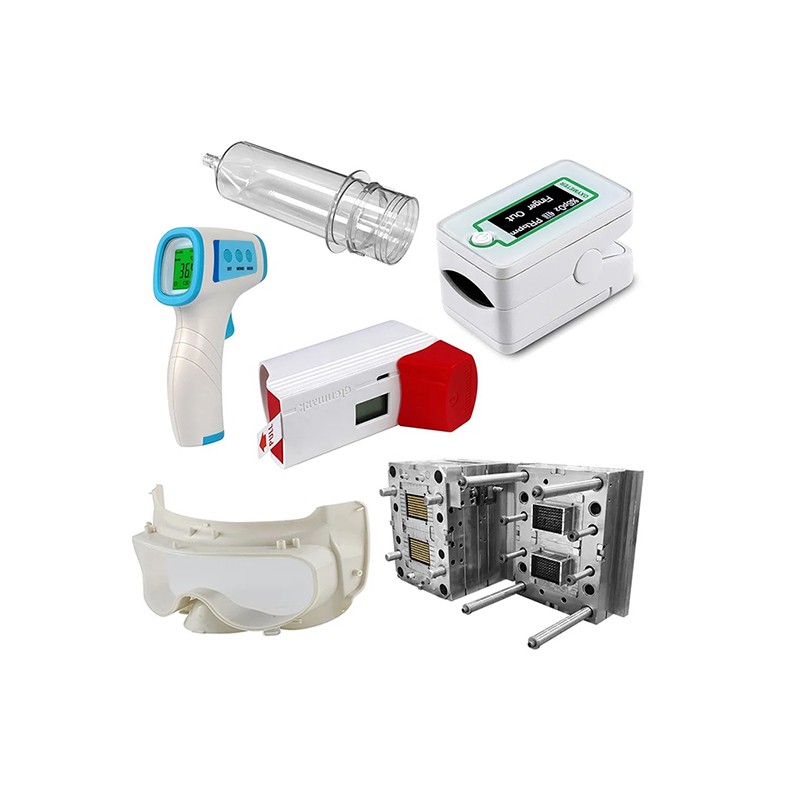
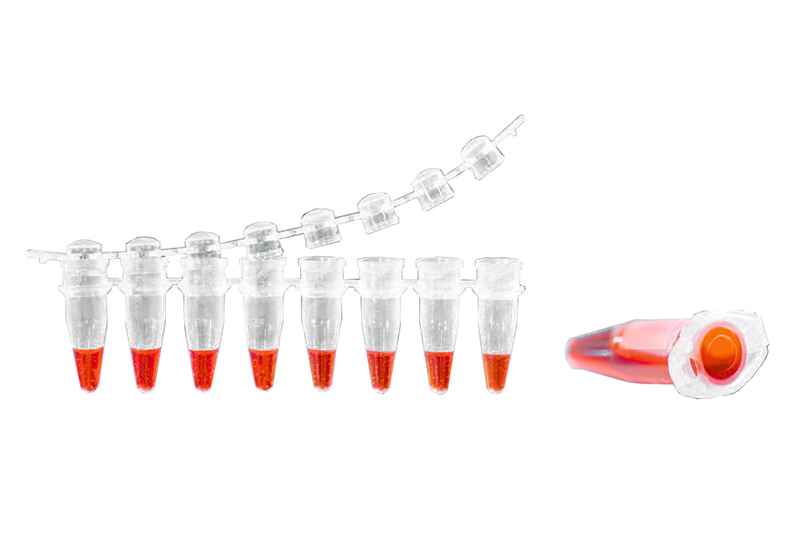
Medical & Health Care
Medical injection molding is an economically effective method for producing medical parts with strict tolerances. It is a manufacturing process for producing plastic medical instruments and components. It involves melting plastic resin pellets and injecting the molten material into molds to form specific shapes. This process allows precise control of the size and shape of the product while adhering to strict quality and regulatory standards.
In the healthcare industry, medical injection molding is essential for producing precise and reliable components. Companies specializing in injection molding medical devices ensure that the highest standards are met, using advanced techniques in medical plastic molding. The process of medical plastic injection molding is crucial for creating parts that meet stringent medical standards. Whether it’s injection molding medical parts or developing specialized medical molding techniques, the focus is always on safety and accuracy. The creation of medical device injection mold designs is vital for manufacturing complex and delicate parts. Medical injection mold processes are tailored to produce high-quality Medical and Health Care components, making medical device plastic injection molding a cornerstone of modern medical manufacturing.
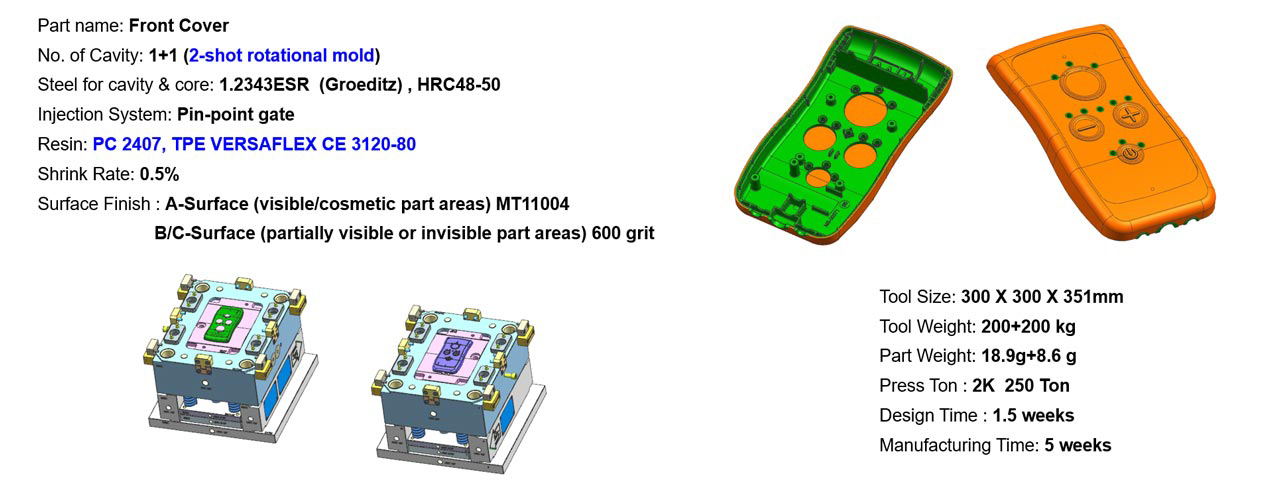
2 Shot Totational Medical Mold Case
Common Medical-Grade Injection Molding Material Options

 Polyethylene (PE):
Polyethylene (PE):
This thermoplastic material with high molecular weight is suitable for wearable medical devices. However, PE cannot be sterilized using high-pressure sterilizers due to its poor heat resistance.
 Polypropylene (PP):
Polypropylene (PP):
PP has high heat resistance, making it ideal for producing parts that require regular sterilization with high-pressure sterilizers. PP is also tough, lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to radiation, chemicals,electricity, and organic solvents.
 Polystyrene (PS):
Polystyrene (PS):
PS offers good impact resistance and dimensional stability. It is non-toxic, affordable, tasteless, FDA-compliant, and lightweight, making it suitable for petri dishes and test tubes.
 Polyetheretherketone (PEEK):
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK):
PEEK has strong chemical resistance, radiation resistance, and wear resistance. Due to its incredible heat resistance, PEEK is suitable for sterilization and injection molding. It is commonly used in orthopedic instruments, dental implants, healing caps, and spinal fusion devices.
 Polycarbonate (PC):
Polycarbonate (PC):
This robust and flexible engineering thermoplastic has high vibration resistance, heat resistance, impact resistance, and UV resistance. PC has good dimensional stability and is commonly used in medical instruments.
Choosing the Right Material for Medical-Grade Products

Choosing materials for medical injection molding involves considering use cases and specific material properties and these features below:
 Durability and Strength:
Durability and Strength:
In the medical industry, using fragile materials is not practical. It’s crucial to select materials resistant to breakage and fracture, providing the required durability and strength for the intended applications.
 Operating Conditions:
Operating Conditions:
Before deciding on a material, the application environment must be considered. For example, if parts need frequent sterilization and exposure to high temperatures, heat-resistant materials like polypropylene should be used. On the other hand, if parts need to be flexible and durable, robust materials like polycarbonate should be chosen.
 Ease of Use:
Ease of Use:
Consider who will be using the part and how it will be used. Cumbersome, ergonomically impractical surgical instruments can hinder surgeons’ work. Lightweight, ergonomic, fully functional, and easy-to-sterilize surgical instruments can play a crucial role.